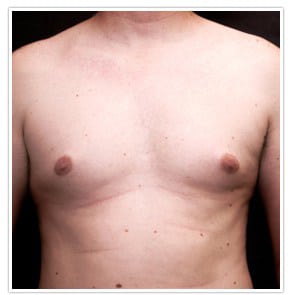
Surgery to correct gynecomastia can be performed on healthy, emotionally stable men of any age, including teenagers. The best candidates for surgery have firm, elastic skin that will reshape to the new contours of the chest.
Surgery may be discouraged for overweight or obese men who have not first attempted to correct the problem with exercise or weight loss. Also, individuals who drink alcoholic beverages in excess or smoke marijuana are usually not considered good candidates for surgery because these substances, along with anabolic steroids, may cause gynecomastia. Therefore, patients are first directed to stop using these drugs to see if the breast enlargement will diminish before plastic surgery is considered an option.
Beyond the risks that accompany all surgery, correction of gynecomastia may produce noticeable scars, permanent pigment changes in the breast area, or slight asymmetry between the two breasts or nipple positions. If the asymmetry is significant, a second procedure may be performed to remove additional tissue.
The Procedure
Gynecomastia surgery is usually done on an outpatient basis, but in extreme cases or when other medical conditions cause concern, an overnight hospital stay may be recommended. The surgery usually takes about 1-1/2 hours (unless more extensive work is needed) and is typically done with general anesthesia.
If an excess of fatty tissue is the primary cause of the breast enlargement, this excess fat will be removed with liposuction. A small incision, less than a half-inch in length, is made around the edge of the areola (the darker skin that surrounds the nipple) or in the armpit area. A slim hollow tube, called a cannula, is inserted through the incision, and the surgeon moves the cannula back and forth through the tissue beneath the skin to break up the fat. The fat is then suctioned out through the cannula, which is attached to a vacuum pump.
In gynecomastia caused by excess glandular tissue, the tissue will be excised (cut out). The excision may be performed alone or in conjunction with a liposuction procedure. In a typical procedure, the excess glandular tissue is removed through the same incisions described for liposuction. If a significant amount of glandular tissue needs to be excised, larger or additional incisions may be required to cut away the excess tissue and skin from around the areola and from the sides and bottom of the breast. In these cases, more conspicuous scars are likely.
If large amounts of fat or glandular tissue have been suctioned out or excised, the skin may not fully contract or tighten to the new chest contour. In these cases, the excess skin can be removed in a later procedure.
Sometimes, a small drain is inserted through a separate incision to draw off excess fluids. Once closed, the incisions are usually covered with a dressing. The chest may be wrapped to keep the skin firmly in place.
What To Expect After Gynecomastia Treatment
Whether you’ve had excision or liposuction, there will be some discomfort for a few days after surgery. This can be controlled with medications prescribed by your surgeon.
Your breast/chest area will be swollen and bruised at first. In fact, you may wonder if there’s been any improvement at all. To help reduce swelling, you’ll probably be instructed to wear an elastic pressure garment continuously for a week or two, and for a few weeks longer at night. Although the worst of the swelling dissipates in the first few weeks, it may be 6 months or more before the final results of surgery are apparent.
You should begin walking around on the day of surgery and can return to work when you feel well enough, which could be as early as a day or two later. Any stitches will be removed within 7 to 10 days after the procedure.
You should avoid sexual activity for 1 to 2 weeks and heavy exercise for about 3 weeks. Also, stay away from any sport or task that risks a blow to the chest area for at least 4 weeks. After about a month, you should be able to resume all your normal activities.
The results of gynecomastia treatment are significant and permanent, and patients with realistic expectations are very satisfied with the outcome.
Gynecomastia FAQ
How Long is Gynecomastia Surgery?
About 1-1/2 hours
What Form of Anesthesia is Used for Surgery?
Usually general
Is Gynecomastia an Inpatient or Outpatient Surgery?
Usually outpatient
What are the Side Effects of Gynecomastia Surgery
Temporary bruising, swelling, numbness, soreness, burning sensation.
What are the Risks of Gynecomastia Surgery?
Infection. Fluid accumulation. Injury to the skin. Rippling or bagginess of skin. Asymmetry. Pigmentation changes (may become permanent if exposed to sun). Loss of nipple sensation. Excessive scarring if tissue or skin is excised. Need for second procedure to remove additional tissue or skin.
How Long is the Recovery Process?
Back to work: 3 to 7 days.
More strenuous activity: 2 to 3 weeks.
Swelling and bruising: 3 to 6 months.
How Long Do the Results of Gynecomastia Surgery Last?
Permanent unless you gain a lot of weight.